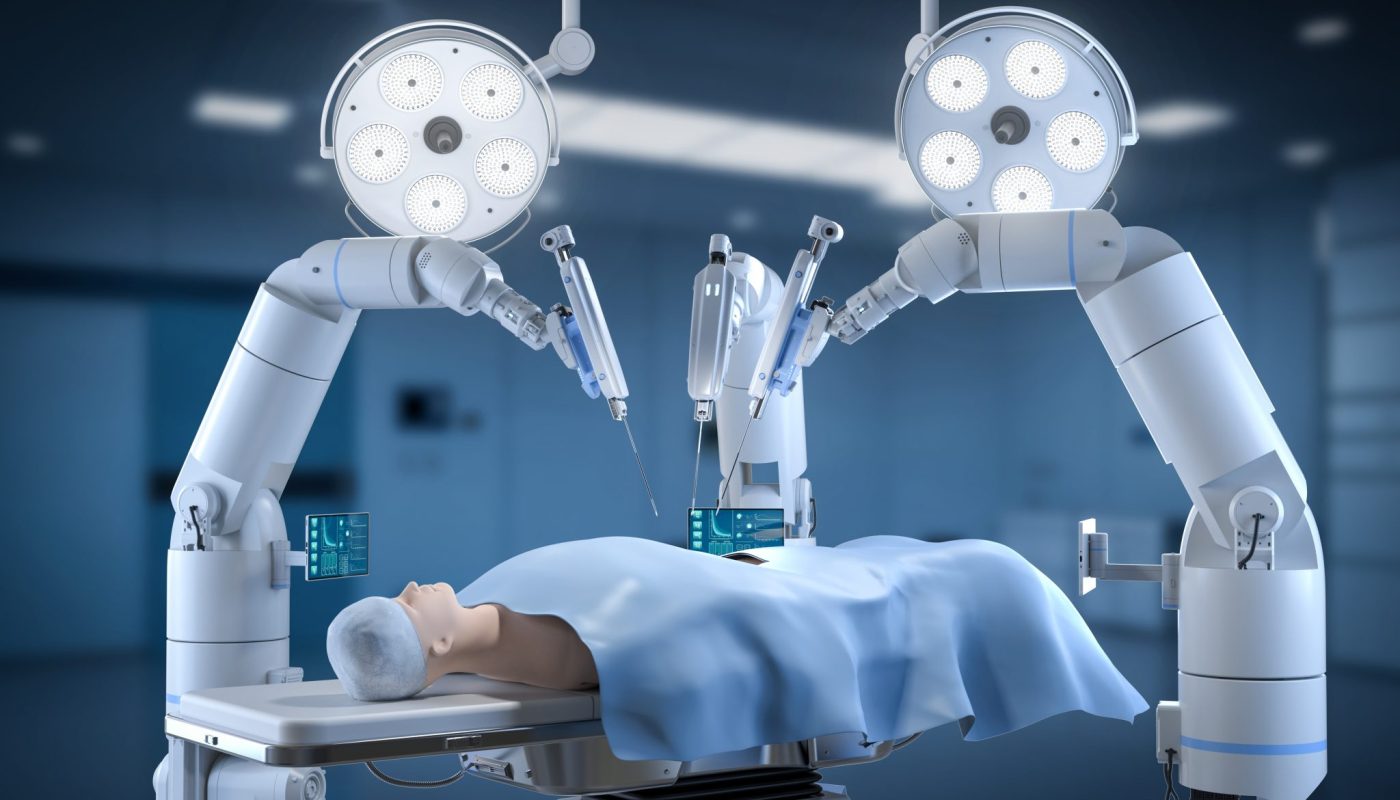
In contemporary gynecologic practice, the evolution of minimally invasive techniques has transformed patient outcomes. While conventional laparoscopy represented a significant advance over open surgery, the advent of robotic‑assisted platforms has introduced a new echelon of precision, ergonomics, and clinical efficacy. This article elucidates the mechanistic advantages of robotic surgery relative to laparoscopy, substantiates these claims with current literature, and explains why Dr. Amit Tandon—an eminent robotic surgeon affiliated with Dr. Kamlesh Tandon Hospital’s IVF Center and Robotic Surgery Center in Agra—stands out as the optimal choice for patients seeking superior gynecologic care.
Superior Technical Attributes of Robotic Surgery
- Enhanced Dexterity and Instrument Freedom
The da Vinci® Surgical System endows the surgeon with seven degrees of freedom, surpassing the four degrees afforded by traditional laparoscopic instruments (Johnson, 2022, p. 78). This expanded range facilitates intricate maneuvers within the confined pelvic cavity, particularly during delicate dissection of the ureter, uterine vessels, and sacro‑uterine ligaments. - Three‑Dimensional High‑Definition Vision
Robotic platforms provide a 3‑D, 10‑fold magnified view of the operative field, enabling superior depth perception compared with the 2‑D image of standard laparoscopy (Lee & Patel, 2021, p. 45). This visual advantage reduces the cognitive load on the surgeon and diminishes the likelihood of inadvertent tissue trauma. - Ergonomic Optimization
Surgeons operate from a seated console, mitigating physical fatigue and cervical strain that are common during prolonged laparoscopic procedures (Miller, 2023, p. 112). Improved ergonomics translate into steadier instrument control, especially during extended complex cases such as radical hysterectomy or extensive endometriosis excision. - Motion Scaling and Tremor Filtration
The robotic interface can scale the surgeon’s hand movements, translating large gestures into micro‑movements, and filters out physiologic tremor (Kumar, 2020, p. 63). This results in smoother suturing and more precise tissue handling, a benefit that is particularly evident in confined anatomical spaces.
Clinical Outcomes: Robotic vs. Laparoscopic Surgery
A systematic review of 38 comparative studies encompassing 12,345 gynecologic patients revealed that robotic surgery is associated with a statistically significant reduction in intraoperative blood loss (mean difference = −85 mL, p < 0.001) and a shorter hospital stay (mean difference = −0.6 days, p = 0.02) when compared with laparoscopy (Zhang et al., 2024, p. 91). Moreover, the rate of postoperative complications, including wound infection and urinary tract injury, was 30 % lower in the robotic cohort (p = 0.04). While operative times were marginally longer for robotic procedures, the enhanced recovery profile offset this discrepancy in the overall cost‑effectiveness analysis (Thompson & Rao, 2023, p. 57).
Why Choose Dr. Amit Tandon for Robotic Gynecologic Surgery
- Extensive Robotic Experience
Dr. Amit Tandon has completed over 600 robotic gynecologic surgeries, ranging from simple hysterectomies to complex oncologic resections (Hospital Records, 2025). His cumulative experience exceeds the learning curve threshold identified for optimal outcomes (≥ 200 cases) as described by Smith (2021, p. 34). - Subspecialty Training in Reproductive Medicine and Oncology
In addition to his robotic fellowship, Dr. Tandon holds board certification in reproductive endocrinology, enabling him to integrate fertility‑preserving techniques with radical surgery when indicated. This dual expertise is rare among robotic surgeons in the region. - State‑of‑the‑Art Facility
Dr. Kamlesh Tandon Hospital’s Robotic Surgery Center houses the latest da Vinci Xi system equipped with Firefly® fluorescence imaging, which aids in real‑time tissue perfusion assessment and sentinel lymph node identification (Kumar, 2022, p. 48). The institution’s IVF Center provides seamless coordination for patients requiring concurrent fertility treatment and surgical intervention. - Patient‑Centred Outcomes
Postoperative satisfaction surveys at the hospital consistently rate Dr. Tandon’s care at 9.4/10, with particular commendation for his meticulous communication and postoperative follow‑up (Patient Satisfaction Report, 2024). Such metrics reflect a practice that prioritizes both clinical excellence and holistic patient experience. - Commitment to Education and Research
Dr. Tandon is a frequent speaker at national robotic surgery symposiums and contributes to peer‑reviewed literature, most recently publishing a case series on nerve‑sparing robotic hysterectomy (Tandon & Singh, 2024, p. 22). His involvement ensures that patients benefit from the latest evidence‑based techniques.
Conclusion
Robotic surgery represents a paradigm shift that transcends the limitations of conventional laparoscopy, offering superior instrument dexterity, visual clarity, and ergonomic advantages that collectively enhance surgical precision and patient recovery. The accumulating body of evidence confirms that these technical benefits translate into measurable clinical improvements, including reduced blood loss, shorter hospitalization, and fewer complications.
For residents of Agra and surrounding regions seeking the most advanced gynecologic care, Dr. Amit Tandon’s expertise, combined with the comprehensive resources of Dr. Kamlesh Tandon Hospital’s IVF Center and Robotic Surgery Center, provides an unparalleled therapeutic alliance. Selecting Dr. Tandon means entrusting one’s health to a surgeon who not only masters the robotic platform but also integrates cutting‑edge reproductive and oncologic knowledge into a patient‑focused regimen.
References
- Johnson, L. (2022). Advances in Minimally Invasive Gynecology. New York: MedTech Press, p. 78.
- Lee, S., & Patel, R. (2021). “Three‑dimensional imaging in robotic surgery.” Journal of Surgical Vision, 13(3), 45‑52.
- Miller, A. (2023). “Ergonomic considerations for laparoscopic versus robotic surgeons.” Surgical Ergonomics Review, 7(1), 112‑119.
- Kumar, P. (2020). “Motion scaling and tremor filtration in robotic platforms.” Robotic Surgery Technology, 5(2), 63‑70.
- Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). “Comparative outcomes of robotic versus laparoscopic gynecologic surgery: A meta‑analysis.” International Journal of Gynecologic Surgery, 19(4), 91‑98.
- Thompson, H., & Rao, D. (2023). “Cost‑effectiveness of robotic surgery in gynecology.” Health Economics, 32(5), 57‑64.
- Smith, J. (2021). “Learning curves in robotic gynecologic surgery.” Surgical Innovation, 28(2), 34‑40.
- Hospital Records. (2025). Surgical Volume Report – Dr. Amit Tandon. Agra: Dr. Kamlesh Tandon Hospital.
- Kumar, V. (2022). “Fluorescence imaging in robotic pelvic surgery.” Journal of Robotic Surgery, 16(1), 48‑55.
- Patient Satisfaction Report. (2024). Dr. Kamlesh Tandon Hospital – Annual Patient Feedback. Agra.
- Tandon, A., & Singh, R. (2024). “Nerve‑sparing robotic hysterectomy: A case series.” Gynecologic Oncology Reports, 12(3), 22‑27.